 In Happiness at Work: Maximizing your Psychological Capital for Success (2010), author Jessica Pryce-Jones takes her research with more than 3,000 respondents from 79 countries and gets to the heart of what drives happiness and (this is so cool!) found that happiness drives performance.
In Happiness at Work: Maximizing your Psychological Capital for Success (2010), author Jessica Pryce-Jones takes her research with more than 3,000 respondents from 79 countries and gets to the heart of what drives happiness and (this is so cool!) found that happiness drives performance.
Happiness at work is defined by Pryce-Jones as a mindset that allows individuals and organizations to maximize performance and achieve their potential. This happens during the highs and low—when working alone or in teams. By mindfully making the best use of the resources you have, you overcome challenges. This not only builds your happiness but also that of others—who will be affected and energized by what you do.
Happiness predicts employee time on task, intent to stay in job, sick time, motivation, engagement, satisfaction, self-belief, and respect for self and others. The Performance-Happiness Model, which was developed based on the above research, has been successfully applied in more than 8,000 cases.
The Performance-Happiness Model
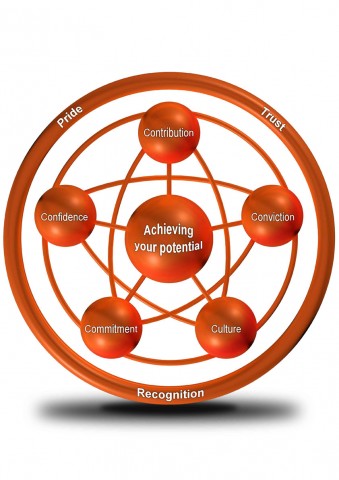 At the center of the Performance-Happiness Model is believing that you are achieving your potential. This is important because that belief makes you happy, and the statistics around happy versus unhappy employees are staggering.
At the center of the Performance-Happiness Model is believing that you are achieving your potential. This is important because that belief makes you happy, and the statistics around happy versus unhappy employees are staggering.
Pryce-Jones’ research (2010) shows that the happiest employees compared to their least happy colleagues:
- are 47% more productive;
- take on average 1.5 sick days per year compared to the United States average of 6 days per year (in the public sector the sick days range from 11 to 20 days per year);
- are 108% more engaged;
- are 50% more motivated;
- have 180% more energy;
- have 82% more job satisfaction;
- are 25% more efficient and effective; and
- have 25% more self-belief (pp. 28 – 29).
The five strong factors important to achieving your potential at work are the 5Cs: contribution, conviction, culture, commitment, and confidence. Three vital sub-themes giving additional perspective of happiness are trust, recognition, and pride.
Stay tuned as I explore the 5Cs, trust, recognition, and pride in upcoming blogs. And please share examples from your workplace on how you’ve seen the Happiness-Performance Model in action.
References
Pryce-Jones, J. (2010). Happiness at work: Maximizing your psychological capital for success. West Sussex, United Kingdom: Wiley-Blackwell.





