
“What do you do?” a new acquaintance asked me the other day. “I’m in the business of changing people’s lives,” I replied.
“Tell me more,” he smiled. “I use co-active coaching, positive psychology and the science of happiness to help people become healthier, more productive and to flourish,” I said.
I followed up by asking him what in his life brings him the greatest joy. “My partner,” he replied. “She is an amazing woman, and we have a wonderful relationship. Every day is a new adventure, and I cherish our every moment together.”
“What would it be like if you could have that passion in other areas of you life—in your career, for example?” I invited him to explore. “It would be great!” he replied. “I’ve never really thought that could be possible. The place I work at is so miserable. While I try to stay positive, there is so much negativity around me when I’m there. I don’t think I can make lemonade out of the lemons I’ve been given at Blankety-Blank Company.”
Isn’t that the way so many people feel? And what a shame. The thing is, each person has the option to control a good deal of his or her own happiness. Here’s where the science of happiness at work comes in. Because we can measure the key drivers of happiness at work (contribution, conviction, commitment, culture, confidence—coupled with trust, recognition and pride), we can focus in on the areas that need a boost. My business, Capiche, does this with individual coaching and team workshops. The results are impressive—both for the individuals and for the company. Individuals gain greater confidence, creativity, energy and job satisfaction. The company gains longer-term employees with 100% greater productivity who take ten times less sick leave, provide better customer service, make more accurate and better decisions, and are better team players.
Are you interested? I’d love to explore how the science of happiness can work for you. I invite you to contact me for a 30-minute sample coaching session to explore your personal happiness—either as it pertains to work or anything else. If you are a team leader and want to explore how your team can be happier, contact me for a free team happiness at work report that shows where your team could use a boost. Nothing to lose. No obligations. No kidding! I’m in the business of changing people’s lives. chris@capiche.us or 541-601-0114


 Have you ever endured a team meeting that went from productive to disastrous? Where the people from the departments that make up the team just didn’t seem to get it? They fought with each other, protected their own departments and were distracted by a bazillion side issues and personal problems? Did you drift off, thinking of Elvis Costello’s plaintive cry, “What’s so funny ‘bout peace, love and understanding?” Does it make you want to go back to the good ol’ days where each department did its job and didn’t have to worry about what was going on in other areas of the organization?
Have you ever endured a team meeting that went from productive to disastrous? Where the people from the departments that make up the team just didn’t seem to get it? They fought with each other, protected their own departments and were distracted by a bazillion side issues and personal problems? Did you drift off, thinking of Elvis Costello’s plaintive cry, “What’s so funny ‘bout peace, love and understanding?” Does it make you want to go back to the good ol’ days where each department did its job and didn’t have to worry about what was going on in other areas of the organization?
 The Science Behind the Smile: Researchers are now measuring happiness and defining what really makes people happy. It’s not what you think. Yes, people who are rich, in a good relationship, actively participating in their church and healthy are happier overall. But events like getting a promotion, a new house or car or acing an exam only create more happiness for about three months. The frequency of positive experiences is more important than the intensity. And at work, what really contributes most to happiness is feeling appropriately challenged—when you’re striving to achieve goals that are ambitious but not out of reach. Managers take note: happier workers are more productive and creative. Years of research on rewards and punishment present a very clear finding: rewards work better.
The Science Behind the Smile: Researchers are now measuring happiness and defining what really makes people happy. It’s not what you think. Yes, people who are rich, in a good relationship, actively participating in their church and healthy are happier overall. But events like getting a promotion, a new house or car or acing an exam only create more happiness for about three months. The frequency of positive experiences is more important than the intensity. And at work, what really contributes most to happiness is feeling appropriately challenged—when you’re striving to achieve goals that are ambitious but not out of reach. Managers take note: happier workers are more productive and creative. Years of research on rewards and punishment present a very clear finding: rewards work better. I’m presenting tomorrow at the University of New Mexico’s Mentoring Institute Conference on Leveraging the Science of Happiness at Work. Excited! Also doing a poster session and getting my paper published in the proceedings. A copy will soon be on this website.
I’m presenting tomorrow at the University of New Mexico’s Mentoring Institute Conference on Leveraging the Science of Happiness at Work. Excited! Also doing a poster session and getting my paper published in the proceedings. A copy will soon be on this website.  In Happiness at Work: Maximizing your Psychological Capital for Success (2010), author Jessica Pryce-Jones takes her research with more than 3,000 respondents from 79 countries and gets to the heart of what drives happiness and (this is so cool!) found that
In Happiness at Work: Maximizing your Psychological Capital for Success (2010), author Jessica Pryce-Jones takes her research with more than 3,000 respondents from 79 countries and gets to the heart of what drives happiness and (this is so cool!) found that 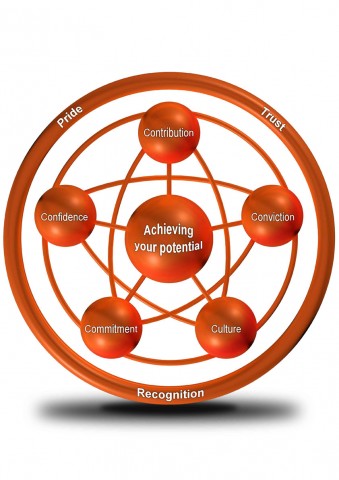 At the center of the Performance-Happiness Model is believing that you are achieving your potential. This is important because that belief makes you happy, and the statistics around happy versus unhappy employees are staggering.
At the center of the Performance-Happiness Model is believing that you are achieving your potential. This is important because that belief makes you happy, and the statistics around happy versus unhappy employees are staggering.


