Pssst … it’s all about happiness!
Last week, I got to present “Critical Factors for Keeping Top Talent” at a SOREDI event. It was fun to share one of my favorite topics—the importance of happiness at work. With Oregon’s unemployment rate at 3.8% and the country’s at 4.3%, SOREDI was smart to focus on such a relevant topic!
The 2017 PwC CEO Survey found the top three CEO challenges in the United States are talent, technology and innovation. About talent, the report states, “Talent will help an organization distinguish itself from the competition. Organizations need people who can surmount big challenges and tackle complex issues. CEOs are looking for employees who are agile, curious, and can collaborate with others to achieve the greatest results. These skill sets are among the hardest to recruit.”
I believe in two simple truths:
- Your people are the #1 resource that will determine your success.
- Happy people perform better.
There are many factors that influence success, but it’s your people who give you an absolute advantage.
Happiness is a worthwhile investment. Decades of compelling evidence shows that improving happiness in the workplace delivers significant increases in profit, productivity and innovation—not to mention substantial cost savings. Happier workers are healthier and more effective team members, and they provide superior customer service. Happier businesses attract top talent and are more likely to retain their best workers.
- 30% Higher productivity1
- 54% Better staff retention2
- 3x Higher creativity3
Social economist and researcher (and all-around good guy) Nic Marks uses a dynamic model to explain which factors create a happy workplace. The model takes into account people’s “experience of work” (how they feel), which is influenced by how they are “functioning at work” (what they do). This depends on the “organizational system” (where they work) and their “personal resources” (who they are). Using an assessment developed by Nic and his company Happiness Works, you can generate your own dynamic model for your workplace.
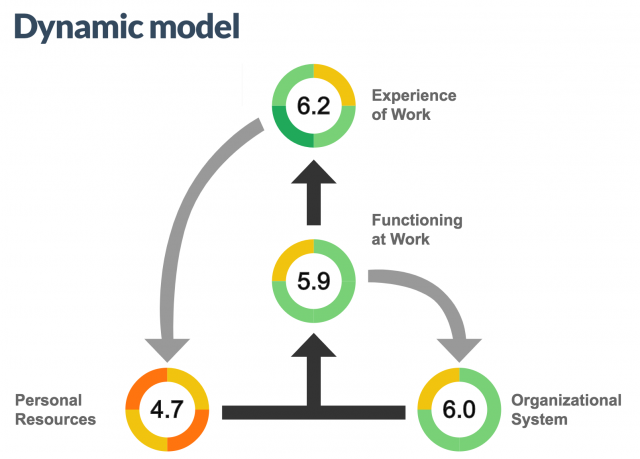
This dynamic model is from a Portland tech company Capiche worked with. Notice the colors ranging from orange to dark green. Like a stoplight, red to orange is a non-starter, and green is a go.
Measured within each of the four components of the dynamic model are:
- Experience of work: Positive and negative feelings, engaging work, worthwhile work
- Functioning at work: Self-expression, sense of control, sense of progress, work relationships
- Organizational system: Job design, management system, work environment, social value
- Personal resources: Vitality, happiness, confidence, work-life integration
People’s happiness at work is not fixed or static; instead, it is fluid and moving, interconnected and dynamic. I like the illustration of shared responsibility between the employee and employer.
People’s happiness at work is not fixed or static; instead, it is fluid and moving. Share on XFinders, Keepers?
The factors you need to keep top talent directly correlate with the factors needed to recruit talent.
Happiness at work isn’t something that’s reserved for companies like Zappos and Google. There are plenty of smaller or lesser-known companies like these Southern Oregon ones that have it right: Coding Zeal, Darex, Bio Skin, and Dutch Bros.
If you are ready to step up to happiness, give me a holler via email or phone at 541.601.0114. Let’s see where you are now and make plans to increase your organization’s happiness—and recruitment, retention, innovation, customer service and profits!
References
- “Insight to impact leadership that gets results.” Hay Group.
- “Engaging hearts and minds: preparing for a changing world.” Hay Group.
- “Positive affect facilitates creative problem solving.” Isen, A.M., Daubman, K.A., and Nowicki, G.P. (1987). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52(6), 1122.














